The Tropical Ecology Assessment and Monitoring (TEAM) network has the aim to measure and compare plants, terrestrial mammals, ground-dwelling birds and climate using a standard methodology in a range of tropical forests, from relatively pristine places to those most affected by people. TEAM currently operates in sixteen tropical forest sites across Africa, Asia and Latin America supporting a network of scientists committed to standardized methods of data collection to quantify how plants and animals respond to pressures such as climate change and human encroachment.
A recent TEAM network paper published in PLOS Biology deals with the standartization of methods in assessing biodiversity trends in tropical forest protected areas.
Abstract:
The 3rd EU BON stakeholder roundtable took place from 10 to 11 December 2015 in Granada, Spain. The meeting brought together participants from global, European and regional projects, institutions, governmental organizations and universities to discuss biodiversity data workflows across different scales. Other important issues to discuss were current limitations of workflows but also tools and products from EU BON and other projects that may help to improve data collection, analysis and use in policy and practice.

Images from the workshop showing participants and group discussions; Credit: Dirk Schmeller/Florian Wetzel
The roundtable focused on EU BON test sites, workflows of data/information and the further usage for policy reporting and political processes. These issues were discussed with partners from EU BON and related biodiversity projects (LTER, GEO BON, Life Watch, Ecoscope) and stakeholders of biodiversity data (regional biodiversity networks: the environmental information network of Andalusia (Rediam), the Center for Monitoring and Assessment of Global Change (CAESCG), the Life project ADAPTAMED as well as local scientists).
On the first day, the different approaches from global (GEO BON) and European projects (EU BON, LTER, Life Watch, Ecoscope) were presented with a special emphasis on data collection, integration and analysis tools from EU BON. Furthermore, regional stakeholders pointed out their demands with regards to data mobilizations issues.
During the second day, discussions focused on the workflow of biodiversity data and the current barriers was discussed and current barriers and possible solutions to overcome the problems. Currently particularly socio-economic data is lacking as well as funding schemes to support interdisciplinary work as well as lacking capacities to address these questions.
In the World Café session, smaller groups discussed details of the workflow, particularly on (1) data mobilization, (2) data and tools, (3) implementation, and (4) upscaling.
As outcomes of the discussions at the round table, several recommendations were drafted, for example, to prioritise developed EU BON tools for further usage in the project and through the portal, to better address the user groups on different levels and provide a detailed and specific description for the tools. There are several biodiversity data workflows existing at the test sites, that could be improved by additional / existing tools, guidelines and standards from projects such as EU BON and by an enhanced communication between local sites, regional networks (as "middle-ware") and European networks.
Overall, it was agreed that a showcase for the workflow of biodiversity data from collection up to visualization (e.g. maps and using user such as the Andalusian Rediam network or/and IPBES as an example) is needed to showcase better the benefits of a European biodiversity network and enhance current functionalities by analyzing barriers and limitations in such an example of an "EU BON storyline".
Presentations:

Picture: Main European networks, projects and regional participants; Credits: Dirk Schmeller/EU projects logos

Introduction from the talk; Credit: Duccio Rocchini
A new paper "Combining internal and external motivations in multi-actor governance arrangements for biodiversity and ecosystem services" published in the journal Environmental Science & Policy looks at ways to motivate actions for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services provision. The paper is a result of the EU FP7 funded project BIOMOT.
This paper analyses the possibility of building a mutually supportive dynamics between internally and externally motivated behaviour for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem services provision. To this purpose a face to face survey amongst 169 key actors of 34 highly successful and prominent biodiversity arrangements in seven EU countries was conducted. The main finding of the paper is the feasibility of combining inherently intrinsically motivated behaviours (providing enjoyment, pleasure from experimentation and learning, aesthetic satisfaction) and internalized extrinsic motivations (related to the identification with the collective goals of conservation policy) through a common set of governance features. Successful initiatives that combine internal and external motivations share the following features: inclusive decision making processes, a broad monitoring by "peers" beyond the core staff of the initiatives, and a context that is supportive for the building of autonomous actor competences. These findings are in line with the psycho-sociological theory of motivation, which shows the importance of a psycho-social context leading to a subjective perception of autonomy and a sense of competence of the actors.
Original Source:
Tom Dedeurwaerdere, Jeroen Admiraal, Almut Beringer, Flavia Bonaiuto, Lavinia Cicero, Paula Fernandez-Wulff, Janneke Hagens, Juha Hiedanpää, Paul Knights, Erica Molinario, Paolo Melindi-Ghidi, Florin Popa, Urban Šilc, Nathalie Soethe, Tiina Soininen, Jose Luis Vivero, Combining internal and external motivations in multi-actor governance arrangements for biodiversity and ecosystem services, Environmental Science & Policy, Volume 58, April 2016, Pages 1-10, ISSN 1462-9011, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2015.12.003
From the 9th to 10th of December 2015 in Granada, Spain EU BON met representatives of LTER Europe. The aim of the meeting was to see where working programmes overlap and whether potential joint products can be identified. In addition the meeting was attended by GEO BON colleagues and included a vision of the upcoming GSEO initiative.
The first day was used to get to know each other and to present first ideas for joint developments. On the second day smaller groups concentrated on three possible joint working areas for the near future:
1) Extended test phase and application of WP3 tools and others
2) Technical/IT aspects, besides others, the use of DEIMS, PlutoF, datasets
3) Development of a manual/best practice for site-based long-term biodiversity observation and monitoring programme
Three working groups will be established and will start their work immediately.
A recently completed benchmark survey of common plants provides a comprehensive dataset of vascular plant diversity and abundance in South Northumberland and Durham, contributing an additional 35,000 observations to the 200,000 observations collected by local recorders since the turn of the millennium.
Apart from contributing an updated inventory of vascular plant diversity, the survey is intended to be used as a reference point with which to identify change in the countryside and study the drivers of biodiversity change in the North-east of England.
Changes in the abundance of rare species have little impact on other species, but change in the abundance of common species can have cascading effects on whole ecosystems. The new survey provides a solid foundation that can be used to qualify the abundance of common species and compare against previous and future studies.
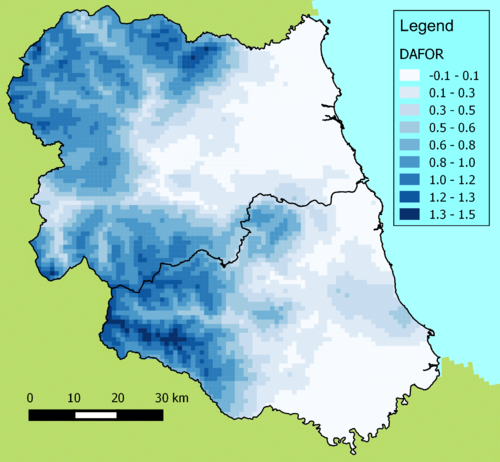
The distribution of heather predicted from the common plant survey data. This is one of the region's most characteristic species and one that many other organisms rely upon for food and cover.
The survey was part of the North-East Common Plants Survey Project, conducted over four years and required volunteers to go to various places. Some surveyed post-industrial brown-field sites, while others walked for miles across bleak moorland to reach sites high in the hills. Although these moors are arguably wilder and natural, the industrial wastelands turn out to be far more biodiverse.
Botanical surveying continues in the region despite the end of the project. Volunteers continue to monitor rare plants in the region and are currently working towards the next atlas of Britain and Ireland, coordinated by the Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland.
This survey is also among the first one to make use of the Integrated Publishing Toolkit (IPT) functionality, jointly developed by EU BON and GBIF, that allows the easy export and exposure of datasets to maximize their discoverability and reuse. The survey was published in the Biodiversity Data Journal, providing easy and streamlined publication of GBIF data via a variety of newly introduced plugins.
Original Source:
Groom Q, Durkin J, O'Reilly J, Mclay A, Richards A, Angel J, Horsley A, Rogers M, Young G (2015) A benchmark survey of the common plants of South Northumberland and Durham, United Kingdom. Biodiversity Data Journal 3: e7318. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.3.e7318
A new article published in the Journal of Marine Science and Engineering looks at how Aphia, the core platform that underpins the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS), can Serve the taxonomic community and the field of biodiversity informatics.
Abstract
The Aphia platform is an infrastructure designed to capture taxonomic and related data and information, and includes an online editing environment. The latter allows easy access to experts so they can update the content of the database in a timely fashion. Aphia is the core platform that underpins the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) and its more than 80 related global, regional and thematic species databases, but it also allows the storage of non-marine data. The content of Aphia can be consulted online, either by individual users or via machine-to-machine interactions. Aphia uses unique and stable identifiers for each available name in the database through the use of Life Science Identifiers (LSIDs). The system not only allows the storage of accepted and unaccepted names, but it also documents the relationships between names. This makes it a very powerful tool for taxonomic quality control, and also allows the linking of different pieces of information through scientific names, both within the Aphia platform and in relation to externally hosted databases. Through these LSIDs, Aphia has become an important player in the field of (marine) biodiversity informatics, allowing interactions between its own taxonomic data and e.g., biogeographic databases. Some applications in the field of biodiversity informatics encompass the coupling of species traits and taxonomy, as well as the creation of diverse, expert validated data products that can be used by policy makers, for example. Aphia also supplies (part of) its content to other data integrators and the infrastructure can be used to host orphan databases in danger of being lost.
Original Source: http://www.mdpi.com/2077-1312/3/4/1448/htm
The Museum für Naturkunde and the Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum are honored to be hosting the 31st Annual Meeting of the Society for the Preservation of Natural History Collections (SPNHC) as well as the 2nd International Conference on Biodiversity Biobanking of the Global Genome Biodiversity Network (GGBN) in Berlin from June, 20 to June, 25, 2016. The conferences will be held in parallel at the andel’s Hotel Berlin, Landsberger Allee.
- SPNHC conference web site: http://www.spnhc2016.berlin/, conference theme: "Green Museum – How to practice what we preach?"
- GGBN conference web site: https://meetings.ggbn.org/conference/ggbn/2016/index, conference theme: "Meeting the Challenge: How to Preserve a Cross-Section of the Tree of Life"
The registration for both conferences is now open. Please check the conference web sites for information on the conference program, field trips, social events, accommodation, registration and abstract submission. All social events and field trips as well as the opening session on Tuesday are joint events for attendees of both conferences. During lunch and coffee breaks one will have the chance to visit the vendor booths and chat with attendees of both conferences. The sessions of both conferences cover complementary topics to avoid duplications.
A new special issue titled "Connecting the Dots: Integrating Biodiversity Observations to Better Track the CBD 2020 Targets" looks at Biodiversity Observatios and the ways that can be integrated into the CBD 2020 targers, for better results in biodiversity conservation.
The issue, where a number of GEO BON partners are authors, explores a wide variety of aspects of Biodiveristy Observations, including data management, integration of in-stiu data, the roles and contricutions of BONs, contextualization with the UN's Sustainable Developmen Goals, and many more.
For more information and to see what is included in the Special Issue, click here.
A joint WP2/3/4/6/7 workshop took place on 23-24 November 2015 in Cambridge, UK. The overall goal of the workshop was to identify synergies and overlapping objectives across WP3/4 and 6/7 and beyond and to thereby identify applications of EU BON’s tools to decision-making, including at the policy level.
The idea for this small, focused workshop emerged as a result of the popularity and outreach achieved by the Aquamaps North-Sea fisheries infographic, developed under WP6. This infographic has demonstrated how the AquaMaps modelling tool can help answer a clear policy or question relevant to decision-making.

Under EU BON, WP3 and WP4 have developed some powerful tools, and more are in the making. The next challenge for EU BON is to use these tools to address policy-relevant issues/questions and to link EU-BON’s modelling capacity to policy needs. Producing cutting-edge innovations is important, but their implementation for policy and decision-making needs is what has real impact.

This is what the Cambridge workshop was about - bringing different players together to identify the right ways to make EU BON innovation policy relevant.
Outcomes of the meeting:
-
An improved vision of how to ‘market’ EU BON’s products for end-users;
-
A better understanding of the end-users and the barriers that they face in accessing and using biodiversity data tools; and
-
Improved collaboration between EU BON Work Packages and a coherent vision for future synergies.
Butterfly monitoring at local, national, regional, and global levels is the topic of the first of the GEO BON Technical Series reports produced to provide stakeholders with practical guidance for biodiversity conservation.
The report is jointly produced by GEO BON, EU BON, UNEP-WCMC, the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) and Dutch Butterfly Conservation, as a follow up of a joint workshop, which took place in December 2014, to catalyse the process for the development of global butterfly monitoring guidelines and the creation of a new specialist butterfly monitoring group.
The report titled "Guidelines for Standardised Global Butterfly Monitoring" provides a suite of standard field protocols that can measure butterfly population change over various spatial and temporal scales, and that can be applied in any part of the world.
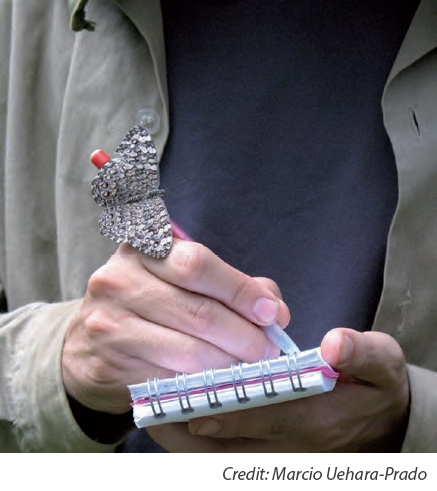

The importance of butterfly monitoring programmes lies in the fact that they provide information about population trends and changes that can be then used as indicators of biodiversity and environmental change outside of the butterfly context.
The guidelines are intended for scheme coordinators, i.e. people wishing to establish butterfly monitoring in any part of the world. The guidelines explain how to set up butterfly monitoring that can provide consistent and comparable results between sites and between years, consistent with international standards.
The ambition behind this new publication is that butterfly populations around the world are well monitored, thereby providing vital information on how these insect populations and other parts of biodiversity are changing. This information is important for feeding into local, national, regional, and global decision-making to help reduce biodiversity loss as well as raising awareness of butterflies and biodiversity in general.
Original Source:
Van Swaay, C., Regan, E., Ling, M., Bozhinovska, E., Fernandez, M., Marini-Filho, O.J., Huertas, B., Phon, C.-K., Kőrösi, A., Meerman, J., Pe’er, G., Uehara-Prado, M., Sáfián, S., Sam, L., Shuey, J., Taron, D., Terblanche, R., and Underhill, L. (2015). Guidelines for Standardised Global Butterfly Monitoring. Group on Earth Observations Biodiversity Observation Network, Leipzig, Germany. GEO BON Technical Series 1, 32pp.
Europe's main zoological taxonomic index - Fauna Europaea presents its updated and modernized website at http://www.fauna-eu.org/. Scientific names and distributions of all living, currently known, multicellular, European land and freshwater animal species are available in one authoritative database.Fauna Europaea offers key information on:
- Taxonomical index for European land and freshwater species
- Information on the geographical distribution of many species
- Database on taxonomic experts in Europe
- References on literature of European species taxonomy and distribution
- A browsable taxon tree

Fauna Europaea provides access to its rich and quality-checked data via this public web portal that also links to other key biodiversity services. It is installed as a taxonomic backbone in a wide range of biodiversity services and actively contributes to biodiversity informatics innovations in various initiatives and EC programs. Fauna Europaea started in 2000 as an EC funded FP5 project and provides a unique taxonomic reference for many user-groups such as scientists, governments, industries, nature conservation communities and educational programs. Fauna Europaea was formally accepted as an INSPIRE standard for Europe, as part of the European Taxonomic Backbone established in PESI. Today it is hosted by the Museum für Naturkunde in Berlin.




 RSS news
RSS news