The Biodiversity Indicators Partnership (BIP) Secretariat is looking for indicators to fill gaps in the global suite of biodiversity indicators and allow a full understanding of progress towards globally agreed targets.
They are inviting experts and organisations to participate in an open online consultation to fill the gaps in the global indicator framework for the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020. Through this short online survey they want to hear about any existing indicators (both global and sub-global in scale), indicators under development, potentially useful datasets or key experts or organisations in the fields. The main focus is on indicators that respond to the gaps in the global framework, which are listed on the attached flyer, but they are also keen to hear about any other indicators that could potentially enhance the existing indicator suite.
The consultation is open until 30 June 2016. Further information on the consultation is available in the attached flyer, the BIP website http://www.bipindicators.net/gaps, and the CBD notification SCBD/OES/RH/KNM/85710.
Set to compile the largest biodiversity data collection for Europe to date, the EU-funded FP7 project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON) has now launched the beta-version of its European Biodiversity Portal.
Despite being a beta version, this release already addresses the main aim to offer a unique service for analysing and understanding biodiversity change in Europe. For instance, users can explore how relative abundance of species (within a larger group) changes over time by using big data mediated by GBIF. There is also a spatial browser for locating datasets in any part of the world, which may be usable for computing the EBVs for species populations.
Additionally, an online analytical data processing (OLAP) toolbox has been included in this release. Based on GEOSS technology, the new portal lets users harvest and simultaneously access data from several directories, including GBIF, LTER, EuMon (coming), PESI, and GEOSS sources.
Started in 2012, the five-year project EU BON has been working towards building this new European Biodiversity Portal where scattered and various information and tools are collected, highlighted and widely shared for future research.
The service will provide all interested parties with a professional database platform with a large amount of implications. For example, coordinators can receive information about related monitoring programs in different countries. Initiatives could integrate their data and compare the trends and status across different countries and regions.
"The ultimate goal of EU BON is to build a comprehensive European Biodiversity Portal that will then feed into a Global Portal currently developed by GEO BON. This initiative will provide a completely new holistic way for analyzing global trends and processes.", concludes Dr. Hannu Saarenmaa, University of Eastern Finland and Work Package leader in EU BON.
We invite everyone to test the new portal and send us their feedback and suggestions for improvements via our Feedback Form.
The 10th GEO European Projects Workshop that took place from 31 May - 2 June, in Berlin, was a success for EU BON in many ways. Among the significant achievements was signing a Memorandum of Understanding with the ConnectinGEO project to add this important initiative to our ever-growing list of associated partners.
The MoU handed over by EU BON coordinator Dr. Christoph Häuser to Dr. Joan Masó, coordinator of ConnectinGEO.

Handing over the MoU between Christoph Häuser, EU BON (left) and Joan Masó, ConnectinGEO (right); Credit: EU BON
ConnectinGEO is under the umbrella of GEOSS and the EU funding with the aim of linking existing coordinated Earth observation networks with the science and technology (S&T) communities, the industry sector and the GEOSS and Copernicus stakeholders. The goal is to facilitate a broader and more accessible knowledge base to support the needs of the GEO Societal Benefit Areas (SBAs) and their users. A broad range of subjects from climate, natural resources and raw materials, to the emerging UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) will be addressed.
Established under the auspices of the UNEP Convention on Migratory Species (UNEP/CMS), the Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and contiguous Atlantic area (ACCOBAMS) is an Intergovernmental Agreement aimed at achieving and maintaining a favorable conservation status for cetaceans though the implementation of coordinated measures.
The Secretariat of ACCOBAMS, based in Monaco, ensures the coordination of the Agreement implementation and provides assistance to the Contracting Parties. In this context, the Secretariat is working on the development of an initiative aimed at responding to the ACCOBAMS strategic objective on improving the understanding of the conservation status of cetaceans at the Mediterranean/Black Sea macroregional level (the "ACCOBAMS Survey Initiative" – ASI).
The overall coordination of the project is provided by the ACCOBAMS Secretariat, according to the mandate given by the Parties to ACCOBAMS, and under the guidance of a Steering Committee. A Scientific Coordinator will be involved in the project for specific tasks/actions related to the scientific aspects of the project.
The Project Officer will ensure the overall coordination of the "ACCOBAMS Survey Initiative" project. He/she will provide operational management of the project, under the general authority of the ACCOBAMS Executive Secretary and the supervision of the ACCOBAMS Project and Fundraising Officer. He/she will also liaise with the Scientific Coordinator.
Due to the exponential growth of biodiversity information in recent years, the questions of how to mobilize such vast amounts of data has become more tangible than ever. Best practices for data sharing, data publishing, and involvement of scientific and citizen communities in data generation are the main topic of a recent report by the EU FP7 project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON), published in the innovative Research Ideas & Outcomes (RIO) journal.
The report "Data sharing tools for Biodiversity Observation Networks" provides conceptual and practical advice for implementation of the available data sharing and data publishing tools. A detailed description of tools, their pros and cons, is followed by recommendations on their deployment and enhancement to guide biodiversity data managers in their choices.
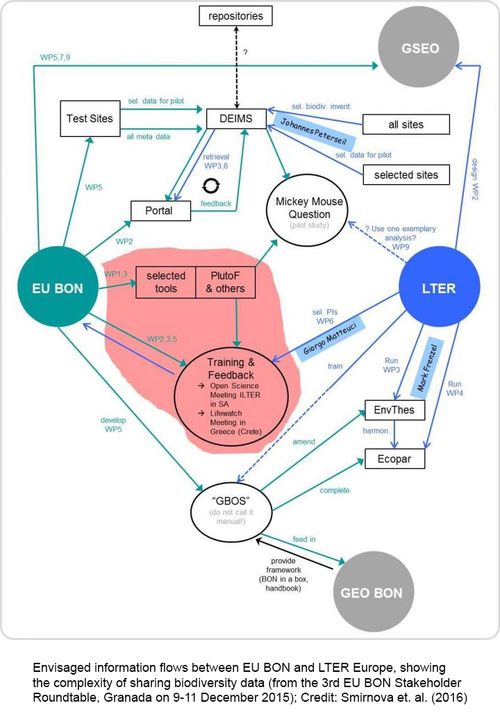
"We believe publishing this report in RIO makes a lot of sense given the journal's innovative concept of publishing unconventional research outcomes such as project reports. This feature provides projects like EU BON with the chance to showcase their results effectively and timely. The report provides a useful practical guide for biodiversity data managers and RIO gives the project an opportunity to share findings with anyone who will make use of such information", explains Prof. Lyubomir Penev, Managing Director of Pensoft and partner in EU BON.
The new report is the second EU BON contribution featured in a dedicated project outcomes collection in RIO. Together with the data policy recommendations it provides a comprehensive set of resources for the use of biodiversity data managers and users.
"We did our biodiversity data sharing tools comparison from the perspective of the needs of the biodiversity observation community with an eye on the development of a unified user interface to this data - the European Biodiversity Portal (EBP)", add the authors.
The scientists have identified two main challenges standing in front of the biodiversity data community. On the one hand, there is a variety of tools but none can as stand alone, satisfy all the requirements of the wide variety of data providers. On the other hand, gaps in data coverage and quality demand more effort in data mobilization.
"For the time being a combination of tools combined in a new work-flow, makes the most sense for EU BON to mobilize biodiversity data," comment the report authors on their findings. "There is more research to be done and tools to be developed, but for the future there is one firm conclusion and it is that the choice of tools should be defined by the needs of those observing biodiversity - the end user community in the broadest sense - from volunteer scientists to decision makers."
Original Source:
Smirnova L, Mergen P, Groom Q, De Wever A, Penev L, Stoev P, Pe'er I, Runnel V, Camacho A, Vincent T, Agosti D, Arvanitidis C, Bonet F, Saarenmaa H (2016) Data sharing tools adopted by the European Biodiversity Observation Network Project. Research Ideas and Outcomes 2: e9390. doi: 10.3897/rio.2.e9390




 RSS news
RSS news



