The GEO XIII Plenary in St. Petersburg enjoyed a huge interest and support from many member governments, agencies and networks with around 400 registered participants this year.
Having taken place from 7-10 November 2016, the event featured a plenary, a number of side events and exhibition to give a chance to participants to meet up and discuss ideas and progress.


Left: The EU BON booth at the GEO exhibition - F. Wetzel, Ch. Häuser, H. Saarenmaa; Right: Director General J.E. Smits and Christoph Häuser; Credits: F. Wetzel
On the sidelines of the Plenary the Director-General for Research and Innovation of the European Commission, Robert-Jan Smits, personally informed himself in a conversation with Dr. Christoph Häuser, project lead of EU BON on the success and performance of the EU BON project.
At the GEO Exhibition 45 participating organizations and agencies presented their current achievements in the realm of earth observation products. EU BON was part of the European Commission’s area where GEO-related projects were shown. The project showcased its latest products as well as provided live demonstrations by Dr. Hannu Saarenmaa of the beta-version of the European Biodiversity Portal.
Taking place just before the plenary, around 20 side events gave an interesting overview of current GEO-related projects and topics. One of the side events was targeted on citizen science and EU-funded projects, where EU BON’s coordinator Christoph Häuser presented the developments of the network with regards to its citizen science activities, particularly its developments of mobile apps for collecting citizen science data.

Christoph Häuser presenting citizen science related activities of EU BON; Credit: F. Wetzel.
Learn more about the portal in the relevant policy brief, or test it at: http://biodiversity.eubon.eu/
For more information about EU BON products and research, you can also watch the project video:
Being voluntary, citizen science work is often automatically assumed to also be openly available. Contrary to the expectations, however, a recent study of the datasets available from volunteers on the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) prove to be among the most restrictive in how they can be used.
There is a high demand for biodiversity observation data to inform conservation and environmental policy, and citizen scientists generate the vast majority of terrestrial biodiversity observations. The analysis on GBIF showed that citizen science datasets comprise 10% of datasets on GBIF, but actually account for the impressive 60% of all observations.
Invaluable as a resource for conservationists and biodiversity scientists, however, these resources unfortunately often come with restrictions for re-use. Although the vast majority of citizen science datasets did not include a license statement, as a whole, they ranked low on the openness of their data.
The assumption that voluntary data collection leads to data sharing is not only not reflecting the real situation, but also does not recognize the wishes and motivations of those who collect data, nor does it respects the crucial contributions of these data to long-term monitoring of biodiversity trends.
In a recent commentary paper, published in the Journal of Applied Ecology, EU BON partners suggest ways to improve data openness. According to the researchers citizen scientists should be recognised in ways that correspond with their motivations, in addition its is advisable that organisations that manage these data should make their data sharing policies open and explicit.
Original Research:
Groom, Q., Weatherdon, L. & Geijzendorffer, I. (2016) Is citizen science an open science in the case of biodiversity observations? Journal of Applied Ecology. DOI: 10.1111/1365-2664.12767
A new EU BON derived paper, publsihed recently in the journal Remote Sensing, introduces eHabitat+, a habitat modelling service supporting the European Commission’s Digital Observatory for Protected Areas.
Abstract:
Protected areas (PAs) need to be assessed systematically according to biodiversity values and threats in order to support decision-making processes. For this, PAs can be characterized according to their species, ecosystems and threats, but such information is often difficult to access and usually not comparable across regions. There are currently over 200,000 PAs in the world, and assessing these systematically according to their ecological values remains a huge challenge. However, linking remote sensing with ecological modelling can help to overcome some limitations of conservation studies, such as the sampling bias of biodiversity inventories. The aim of this paper is to introduce eHabitat+, a habitat modelling service supporting the European Commission’s Digital Observatory for Protected Areas, and specifically to discuss a component that systematically stratifies PAs into different habitat functional types based on remote sensing data. eHabitat+ uses an optimized procedure of automatic image segmentation based on several environmental variables to identify the main biophysical gradients in each PA. This allows a systematic production of key indicators on PAs that can be compared globally. Results from a few case studies are illustrated to show the benefits and limitations of this open-source tool.
Original Source:
Martínez-López, J.; Bertzky, B.; Bonet-García, F.J.; Bastin, L.; Dubois, G. Biophysical Characterization of Protected Areas Globally through Optimized Image Segmentation and Classification. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 780. DOI: 0.3390/rs8090780
Key in ensuring the effectiveness of conservation efforts and maintaining ecosystem health, measuring biodiversity can benefit greatly when remote sensing data comes into the equation. A new EU BON related paper, published in the journal Ecological Indicators, proposes open source solutions for measuring the important Rao's Q index, when it comes to remote sensing data.
Measuring biodiversity is a key issue in ecology to guarantee effective indicators of ecosystem health at different spatial and time scales. However, estimating biodiversity from field observations might present difficulties related to costs and time needed. Moreover, a continuous data update for biodiversity monitoring purposes might be prohibitive. From this point of view, remote sensing represents a powerful tool since it allows to cover wide areas in a relatively low amount of time. One of the most common indicators of biodiversity is Shannon's entropy H′, which is strictly related to environmental heterogeneity, and thus to species diversity. However, Shannon's entropy might show drawbacks once applied to remote sensing data, since it considers relative abundances but it does not explicitly account for distances among pixels’ numerical values. In this paper we propose the use of Rao's Q applied to remotely sensed data, providing a straightforward R-package function to calculate it in 2D systems. We will introduce the theoretical rationale behind Rao's index and then provide applied examples based on the proposed R function.
Original Source:
Rocchini, D., Marcantonio, M., Ricotta, C. (2017). Measuring Rao's Q diversity index rom remote sensing: an open source solution. Ecological Indicators, 72: 234-238. [5years-IF: 3.649] DOI:10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.039
The EU project EKLIPSE has joined our family of associated partners. The MoU was signed by Dr. Carsten Neßhöver, UFZ, on behalf of EKLIPSE project Coordinator Dr. Allan Watt (NERC-Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Edinburgh, UK) and Dr. Anke Hoffmann, on behalf of EU BON Coordinator Dr. Christoph Häuser, during the 2016 GEO BON Open Science Conference & All Hands Meeting in Leipzig, Germany.

Dr. Carsten Neßhöver and Dr. Anke Hoffmann at the handing of the MoU; Credit: EKLIPSE
EKLIPSE is a EU project that will set up a sustainable and innovative way of knowing, networking and learning about biodiversity and ecosystem services. EKLIPSE is an unusual project in several ways, particularly:
-
The project is funded for four years to develop a sustainable mechanism that will be in place for many years to come.
-
The development of the support mechanism through the project is facilitated by project partners. Their role is to facilitate linkages between science, policy and society, through different actions, such as knowledge synthesis, identifying research priorities, and building the Network of Networks that will support the other actions.
A recent article in the academic journal Science published by Prof. Urmas Kõljalg and colleagues aims to explain the possibilities for identifying species determined based on DNA samples only.
The article was published as a response to David Hibbetts paper "The invisible dimension of fungal diversity". The American mycologist Hibbett argues that huge amount of fungal species cannot be identified and described scientifically as the international code does not permit describing new species based on DNA samples derived from molecular surveys of the environment. However, the Estonian and Swedish scientists show – analysing the same data – how DNA based fungal species have been identified and communicated for several years now using database UNITE (https://unite.ut.ee).

In the forests of Laos the mushroom season has already begun. Among the mushrooms presented on these dishes one can most likely also find species scientifically yet undescribed. The digital object identifiers (DOIs) system created by the scientists in Tartu permits comunication of these species already before they have been granted scientific names. Writing about poisonous mushrooms for example helps to keep people informed, so that cases of intoxication can be avoided more often. (Photo: Urmas Kõljalg)
"Traditionally species are determined based on their morphology and anatomy, in printed books – traditional keys to nature – species are displayed on pictures and in written descriptions. But DNA of fungi can also be found in samples of soil, of leaves, of air, in these circumstances we do not actually have the fungus itself and we cannot identify it visually," Urmas Kõljalg explains the core of the matter. "In this case, species can be determined evaluating their DNA sequences."
The UNITE Species Hypotheses approach demonstrates how the DNA based fungal species can be referred to in a proper scientific manner already before they have been described formally according to the code. This can be done using unique digital object identifiers (DOIs) given to all fungal species in the UNITE database. This keeps all the references automatically connected and machine-readable by other databases as well.
"Even if the species will have its name ten years from now, the DOI code will help us go back and see, where the species was first described and who found it," Urmas Kõljalg says.
For several years now by leading species classification platforms based on DNA sequences more than half a million DOI codes have been used as identifiers of fungal species. UNITE fungal codes are used by the most influential gene bank NCBI also. The UNITE system uses a new paradigm in identifying species, this paradigm was first described by Urmas Kõljalg and colleagues in 2013.
UNITE – the global unified system for the DNA based fungal species – contains information of all the fungal species known from sequence data, hundreds of researchers from all over the world are collaborating. UNITE is hosted by PlutoF cloud, which permits creating very complex databases for various biodiversity data, including DOIs. The development of PlutoF system is supported by the Estonian research infrastructures roadmap project NATARC (http://natarc.ut.ee), EU BON (http://eubon.eu), etc. All scientists can use PlutoF for free.
EU projects EuMon and EU BON call out to monitoring programs to share data and expertise for building the European Biodiversity Portal.
Combining forces, two large scale EU projects, EuMon and EU BON, are set to compile the largest data collection on biodiversity monitoring activities in Europe to date. Using existing biodiversity data and metadata collected by the two projects, the initiative is a stepping stone in completing a comprehensive European Biodiversity Portal. The projects now call out to monitoring programs across the Old Continent and beyond, to join in, provide information about their schemes and share their expertise for the cause.
For its life span between 2004 and 2008 the project EU-wide monitoring methods and systems of surveillance for species and habitats of Community interest (EuMon) created Europe's most comprehensive metadata catalogue of biodiversity monitoring activities.
Started in 2012, the five-year project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network(EU BON) has been working towards building a new European Biodiversity Portal where this information is collected, highlighted and widely shared for future research and applied biodiversity conservation. The beta version is now all set up and available to test here.


To answer knowledge gaps since the project has ended in 2008, the original EuMon monitoring meta database is being further expanded with new information on data availability and access, as well as with new remote sensing data. Previously underrepresented, the marine realm is now also included in the EuMon collection.
"Monitoring data has received a central stage in recent years, a process largely facilitated by the instalment of the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). However, while knowledge about monitoring efforts is important, we still miss a large variety of available programs and biodiversity data", explains EuMon's Project Leader Prof. Dr. Klaus Henle, Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ.
"We, therefore, currently aim to increase and update the number of monitoring programs in the EuMon catalogue, as the catalogue still covers less than half of all existing programs in Europe", adds EuMon Project Coordinator, Dirk Schmeller, UFZ.
In a joint initiative EuMon and EU BON are now looking to create the opportunity for monitoring program coordinators to publish their data by using the data publishing service of the EU BON portal (data embargos also possible).
The service will provide all interested parties with a professional database platform with a large amount of implications. For example, coordinators can receive information about related monitoring programs in different countries. Initiatives could integrate their data and compare the trends and status across different countries and regions. Volunteers can find contacts about schemes in their regions they may consider to join.
Using the data publishing service of EU BON will also facilitate data sharing with the Global Biodiversity Information Facility.
"The ultimate goal of EU BON is to build a comprehensive European Biodiversity Portal that will then feed into a Global Portal currently developed by GEO BON. This initiative will provide a completely new holistic way for analyzing global trends and processes. We invite projects from across Europe to publish their datasets via the European Biodiversity Portal and become a part of this one-of-a-kind initiative", concludes Dr. Hannu Saarenmaa, University of Eastern Finland and Work Package leader in EU BON.
How to take part:
To access the EuMon database, please visit http://eumon.
The EU BON workshop "Biodiversity research for and by citizens in Eastern Europe: tools, information services and public engagement" was organized to present the EU BON citizen science gateway, share accomplishments of the project, promote products, raise and discuss challenges of citizen science and facilitate networking between countries, especially eastern and central European countries.

There were 33 participants from Baltic countries and Finland and EU BON partners from Norway, Spain, Israel and Brussels. First day was showcasing the citizen science initiatives in Estonia, following best practice examples from EU BON consortium. During the second day the participants got a chance to learn the tools and methods for citizen science data management by ECSA and EU BON. This was followed by world cafe style discussion about the needs of citizen science initiatives and Pan-European citizen science gateway. One of the important conclusions for Baltic countries is that there is a need for stronger collaboration and supportive infrastructure to make citizen science more effective and also deliver accessible data to research community.
Some workshop participants also took part of Tartu Mini-BioBlitz on 29th June, first BioBlitz in Estonia. BioBlitz participants observed 239 species of animals, plants and fungi .
.
Read a first hand report form the workshop in the two great blog posts by Egle Marija Ramanauskaite (a workshop participant from Lithuania):
http://seplute.tumblr.com/post/146841955105/citsci-overtakes-the-baltics-citizen-science
http://seplute.tumblr.com/post/146844410470/citizen-science-workshop-in-tartu-recap-of-day-2
A new opinion piece published in the journal Global Change Biology looks at the development of biodiversity scenarios and their inclusion of future land-use changes.
Abstract:
The 10th GEO European Projects Workshop took place from 31 May until 2 June 2016 in Berlin, Germany. Representatives from science, business and public administration met in Berlin to discuss how European Earth observation initiatives can contribute to the Global Earth Observations System of Systems (GEOSS).
The workshop, was jointly organised by the European Commission, the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure of Germany, and the Museum für Naturkunde - Leibniz Institute for Evolution and Biodiversity Science. A wide range of events gave projects the opportunity to showcase their work and findings and discuss the future of earth observations. The event also featured a series of world cafés where, in a more informal and relaxed environment, experts could discuss topics focused on different aspects and challenges for biodiversity and ecosystem observation for the next ten years.

Group photo of the participants at the 10th GEO European Projects Workshop; Credit: H. Götz
During the meeting EU BON was presented at a specialized session focusing on the "Challenges for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Observation for the Next Ten Years". EU BON’s co-ordinator Dr. Christoph Häuser alongside project partner and WP2 leader Dr. Hannu Saarenmaa presented the latest project developments and results.
#GEPW16 @EUBON1 Christoph Häuser: gaps in biodiversity data in Europe pic.twitter.com/4j02nlUUxJ
— ENEON (@ENEONetwork) June 2, 2016
Special attention was paid to presenting and explaining the functionalities of the recently launched beta version of the EU BON European Biodiversity Portal, which aims to provide a substantial part of GEO BON’s Global Portal.



Clockwise from top left: Dr. Christoph Häuser presenting EU BON; Audience of the 10th GEO Projects Workshop; Panel at the Biodiversity and Ecosystem session; Credits: Florian Wetzel, Hwaja Götz and Anke Hoffmann.
For further information see:
Find out more resources on the official event webpage.
Set to compile the largest biodiversity data collection for Europe to date, the EU-funded FP7 project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON) has now launched the beta-version of its European Biodiversity Portal.
Despite being a beta version, this release already addresses the main aim to offer a unique service for analysing and understanding biodiversity change in Europe. For instance, users can explore how relative abundance of species (within a larger group) changes over time by using big data mediated by GBIF. There is also a spatial browser for locating datasets in any part of the world, which may be usable for computing the EBVs for species populations.
Additionally, an online analytical data processing (OLAP) toolbox has been included in this release. Based on GEOSS technology, the new portal lets users harvest and simultaneously access data from several directories, including GBIF, LTER, EuMon (coming), PESI, and GEOSS sources.
Started in 2012, the five-year project EU BON has been working towards building this new European Biodiversity Portal where scattered and various information and tools are collected, highlighted and widely shared for future research.
The service will provide all interested parties with a professional database platform with a large amount of implications. For example, coordinators can receive information about related monitoring programs in different countries. Initiatives could integrate their data and compare the trends and status across different countries and regions.
"The ultimate goal of EU BON is to build a comprehensive European Biodiversity Portal that will then feed into a Global Portal currently developed by GEO BON. This initiative will provide a completely new holistic way for analyzing global trends and processes.", concludes Dr. Hannu Saarenmaa, University of Eastern Finland and Work Package leader in EU BON.
We invite everyone to test the new portal and send us their feedback and suggestions for improvements via our Feedback Form.
The 10th GEO European Projects Workshop that took place from 31 May - 2 June, in Berlin, was a success for EU BON in many ways. Among the significant achievements was signing a Memorandum of Understanding with the ConnectinGEO project to add this important initiative to our ever-growing list of associated partners.
The MoU handed over by EU BON coordinator Dr. Christoph Häuser to Dr. Joan Masó, coordinator of ConnectinGEO.

Handing over the MoU between Christoph Häuser, EU BON (left) and Joan Masó, ConnectinGEO (right); Credit: EU BON
ConnectinGEO is under the umbrella of GEOSS and the EU funding with the aim of linking existing coordinated Earth observation networks with the science and technology (S&T) communities, the industry sector and the GEOSS and Copernicus stakeholders. The goal is to facilitate a broader and more accessible knowledge base to support the needs of the GEO Societal Benefit Areas (SBAs) and their users. A broad range of subjects from climate, natural resources and raw materials, to the emerging UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) will be addressed.
Due to the exponential growth of biodiversity information in recent years, the questions of how to mobilize such vast amounts of data has become more tangible than ever. Best practices for data sharing, data publishing, and involvement of scientific and citizen communities in data generation are the main topic of a recent report by the EU FP7 project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON), published in the innovative Research Ideas & Outcomes (RIO) journal.
The report "Data sharing tools for Biodiversity Observation Networks" provides conceptual and practical advice for implementation of the available data sharing and data publishing tools. A detailed description of tools, their pros and cons, is followed by recommendations on their deployment and enhancement to guide biodiversity data managers in their choices.
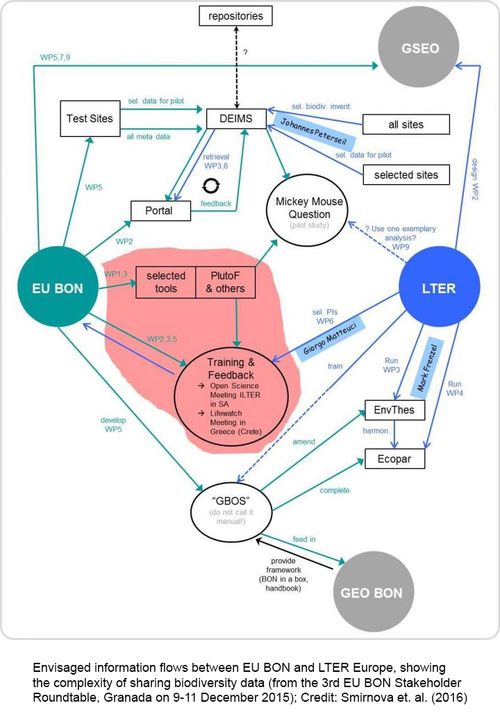
"We believe publishing this report in RIO makes a lot of sense given the journal's innovative concept of publishing unconventional research outcomes such as project reports. This feature provides projects like EU BON with the chance to showcase their results effectively and timely. The report provides a useful practical guide for biodiversity data managers and RIO gives the project an opportunity to share findings with anyone who will make use of such information", explains Prof. Lyubomir Penev, Managing Director of Pensoft and partner in EU BON.
The new report is the second EU BON contribution featured in a dedicated project outcomes collection in RIO. Together with the data policy recommendations it provides a comprehensive set of resources for the use of biodiversity data managers and users.
"We did our biodiversity data sharing tools comparison from the perspective of the needs of the biodiversity observation community with an eye on the development of a unified user interface to this data - the European Biodiversity Portal (EBP)", add the authors.
The scientists have identified two main challenges standing in front of the biodiversity data community. On the one hand, there is a variety of tools but none can as stand alone, satisfy all the requirements of the wide variety of data providers. On the other hand, gaps in data coverage and quality demand more effort in data mobilization.
"For the time being a combination of tools combined in a new work-flow, makes the most sense for EU BON to mobilize biodiversity data," comment the report authors on their findings. "There is more research to be done and tools to be developed, but for the future there is one firm conclusion and it is that the choice of tools should be defined by the needs of those observing biodiversity - the end user community in the broadest sense - from volunteer scientists to decision makers."
Original Source:
Smirnova L, Mergen P, Groom Q, De Wever A, Penev L, Stoev P, Pe'er I, Runnel V, Camacho A, Vincent T, Agosti D, Arvanitidis C, Bonet F, Saarenmaa H (2016) Data sharing tools adopted by the European Biodiversity Observation Network Project. Research Ideas and Outcomes 2: e9390. doi: 10.3897/rio.2.e9390




 RSS news
RSS news

