The GEO-XII Plenary and Ministerial Summit, as well as many associated meetings and events were hosted by the Mexican Government and took place in Mexico City from 9 to 13 November 2015.
The five-day event brought together GEO member countries and organizations, as well as scientists and stakeholders from across the world to debate the next decade for GEO, and to discuss the latest developments in Earth Observation technologies and applications. The GEO-XII Plenary approved the GEO Strategic Plan 2016-2025, and the Summit endorsed a Mexico City Declaration (see: http://www.earthobservations.org/geo12.php).

Mexican music and folklore performances at the hosted conference dinner at GEO-XII; Credit: Hannu Saarenmaa
EU BON participated at GEO-XII and was represented at the European Commission Stand "Europe for GEOSS" with a poster and a short video clip. A real highlight was the visit by the European Commissioner for Research, Science and Innovation, Carlos Moedas. During his short visit, the Commissioner took specific interest in the project and spent some time discussing EU BON's relevance with the coordinator and his staff.


The EC stand "Europe for GEOSS" at GEO-XII, and discussions on EU BON with Commissioner Carlos Moedas; Credits: Jose Miguel Rubio Iglesias (left), Helmut Staudenrausch (right)
EU BON was also presented during a dedicated side event entitled "The GEO Biodiversity Observation Network (GEO BON): Enhancing Biodiversity Observations and Products for User Needs". The project’s key products were introduced by the project coordinator Christoph Häuser and the workpackage 2 leader Hannu Saarenmaa.
From 9 to 11 November in Vienna, Austria the EU H2020 project Detecting changes in essential ecosystem and biodiversity properties – towards a Biosphere Atmosphere Change Index: BACI has organised a special workshop titled "Remote sensing applications related to land use/change" with the aim to facilitate co-design and co-production of knowledge with regard to innovative applications of remote sensing products.
EU BON project partner Duccio Rocchini was among the invited lecturers at the event. His talk titled "Like in a Rubik’s cube: Recomposing Biodiversity Information by Remote Sensing Data" introduced some experience from EU BON.

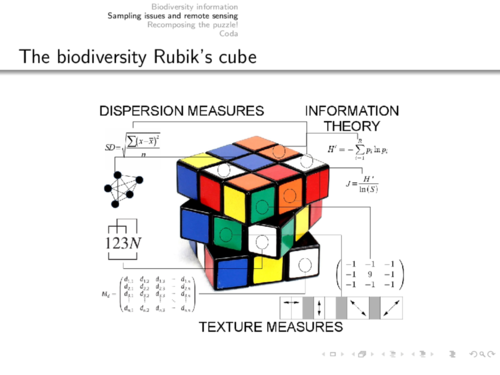
The overarching objective of BACI is to tap into the unrealized potential of existing and scheduled space-borne Earth observation data streams to detect changes in ecosystem functioning and services that have repercussions for essential biodiversity variables, land use potentials, and land-atmosphere interactions.
We are happy to announce the latest member of our Associated Partners list - MUSE (Museo delle Scienze).
MUSE, or the Science Museum is an auxiliary body of the Autonomous Province of Trento. Its task is to interpret nature, starting from the mountains, using the eyes, tools, and applications of scientific research, taking advantage of the challenges of the contemporary world, stimulating scientific curiosity and the pleasure of knowledge, giving value to science, innovation, and sustainability.
We look forward to more institutions and projects joining our Associated Partners family.
The European Commission has recently released publication focused on Earth Observation Research and EU BON is one of the successful projects featured in it.
The publication titled "Investing in European success – A Decade of Success in Earth Observation Research and Innovation" looks at the benefits that Earth Observation brings to studying and protecting the environment.
The Earth’s atmosphere, oceans and landscapes are changing rapidly, with human activities being a major driver. Monitoring and modelling these changes are critical because they allow governments, society and the private sector to make informed decisions about climate, energy, food security, natural hazards, health and other societal challenges. To be effective, these responses must be grounded in comprehensive and timely information. More importantly, decision makers, managers and experts must have access to the information they need, when they need it and in a format which can be easily utilised.
To address this challenge, the intergovernmental Group on Earth Observations (GEO) has provided a voluntary framework since 2005 where 98 governments, the European Commission and 87 international organisations develop new projects and coordinate their strategies and investments in the field of Earth observation. The vision of GEO is to realise a future wherein decisions and actions for the benefit of humankind are informed by coordinated, comprehensive and sustained Earth observations and information. GEO’s main objective is to develop and implement the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS).
EU BON is an attempt to overcome these problems at European level and to contribute to the Group on Earth Observations’ (GEO) global initiative with the same aims – GEO BON.
Find the full publication here, EU BON can be found featured on pages 26 - 27.
How can we monitor Europe-wide farmland biodiversity so that it makes sense to farmers, is ecologically credible and scientifically sound and can be implemented for a reasonable price? Two new studies answer these questions.
First, stakeholders were asked, which indicators provided best "value for money" for their purpose. Habitat, plant species and farm management indicators ranked highest. Wild bees, earthworms and spiders as important providers of ecosystem services came next. Together they form a minimum set of indicators which provides non-redundant information and which can make dominant changes in farmland biodiversity visible.
Researchers from the FP7 funded EU projects "Biodiversity Indicators for European Farming Systems (BioBio)" and "Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON)", then developed cost estimates for nine monitoring scenarios and the authors conclude that a continent-wide farmland biodiversity monitoring scheme would require only a modest share of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) budget (2014-2020).
Cost assessments showed that the farmland biodiversity monitoring scenarios require 0·01% - 0·74% of the total CAP budget and 0·04% - 2·48% of the CAP budget specifically allocated to environmental targets. With 30% of the CAP devoted to environmental targets (more than 120 billion EURO), investing in a monitoring process seems a logical choice given these results. The researchers provide a framework for individual countries to start farmland biodiversity monitoring, building towards a coherent European picture.
The studies were published in the Journal of Applied Ecology and the Journal of Environmental Management.
"Despite scientific proof that monitoring increases the (cost) efficiency of policy measures, monitoring rarely gets included in policy programme budgets. We identified that the cost are not as high as feared. To further facilitate implementation, the study provides stepping stones to build a European monitoring scheme, offering a choice in indicators and using regions as a unit of trend analysis," explains Dr. Ilse Geijzendorffer, the lead author of the Journal of Applied Ecology paper.
Original Source:
Geijzendorffer, I. R., Targetti, S., Schneider, M. K., Brus, D. J., Jeanneret, P., Jongman, R. H.G., Knotters, M., Viaggi, D., Angelova, S., Arndorfer, M., Bailey, D., Balázs, K., Báldi, A., Bogers, M. M. B., Bunce, R. G. H., Choisis, J.-P., Dennis, P., Eiter, S., Fjellstad, W., Friedel, J. K., Gomiero, T., Griffioen, A., Kainz, M., Kovács-Hostyánszki, A., Lüscher, G., Moreno, G., Nascimbene, J., Paoletti, M. G., Pointereau, P., Sarthou, J.-P., Siebrecht, N., Staritsky, I., Stoyanova, S., Wolfrum, S., Herzog, F. (2015), How much would it cost to monitor farmland biodiversity in Europe?.Journal of Applied Ecology. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12552
S. Targetti, F. Herzog, I.R. Geijzendorffer, P. Pointereau, D. Viaggi, Relating costs to the user value of farmland biodiversity measurements, Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 165, 1 January 2016, Pages 286-297, ISSN 0301-4797, http://dx.
Substantial amount of documented occurrence records is awaiting publication stored in repositories and data indexing platforms, such as the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD Systems), or Integrated Digitized Biocollections (iDigBio). In order to streamline the authoring process, save taxonomists time, and provide a workflow for peer-review and quality checks, Pensoft has introduced an innovative feature that makes it possible to easily import occurrence records into a taxonomic manuscript.
Prior to this development, Pensoft's ARPHA Writing Tool (AWT) only used the "upload from Excel" approach for this workflow. Although this method significantly simplified the process of importing materials and is actively used by the authors, it still required one extra transposition step.

Now, we added a new even more user-friendly option. By simply specifying an identifier (ID) in the relevant box, the new import plugin allows for occurrence data, stored at GBIF, BOLD systems, or iDigBio, to be be directly inserted into the manuscript. It all happens in the user-friendly environment of the AWT, where the imported data can be then edited before submission to the Biodiversity Data Journal.
Not having to retype or copy/paste species occurrence records, the authors save a lot of efforts. Moreover, they automatically import them in a structured Darwin Core format, which can be easily downloaded from the article text into structured data by anyone who needs the data for reuse after publication.
Another important aspect of the workflow is that it will serve as a platform for peer-review, publication and curation of raw data, that is of unpublished individual data records coming from collections or observations stored at GBIF, BOLD and iDigBio.
The work has been partially supported by the EC-FP7 EU BON project (ENV 308454, Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network) and the ITN Horizon 2020 project BIG4(Biosystematics, informatics and genomics of the big 4 insect groups: training tomorrow's researchers and entrepreneurs), under Marie Sklodovska-Curie grant agreement No. 542241.
Data collection and analysis are at the core of modern research, and often take months or even years during which researchers remain uncredited for their contribution. A new plugin to a workflow previously developed by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and Pensoft, and tested with datasets shared through GBIF and DataONE, now makes it possible to convert metadata into a manuscript for scholarly publications, with a click of a button.
Pensoft has currently implemented the feature for biodiversity, ecological and environmental data. Such records are either published through GBIF or deposited at DataONE, from where the associated metadata can be converted directly into data paper manuscripts within the ARPHA Writing Tool, where the authors may edit and finalize it in collaboration with co-authors and peers and submit it to the Biodiversity Data Journal (BDJ) with another click. Until now, the GBIF metadata have been exported into an RTF file. The new feature will be also part of future Pensoft projects, including the recently announced Research Ideas & Outcomes (RIO) Journaland the forthcoming Ecology and Sustainability Data Journal.
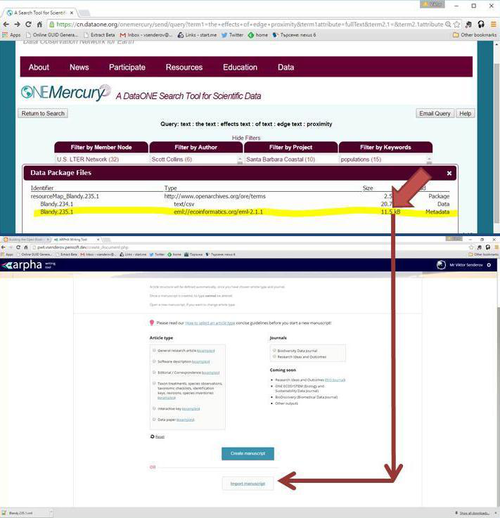
Metadata can be directly downloaded from the repository site (example with ONEMercury from DataONE) and then imported via the ARPHA Writing tool; Credit: ONEMercury, a tool by DataONE
The concept of the data paper was introduced in the early 2000's by the Ecological Society of America in order to solve issues of handling big data and to make the metadata and the corresponding datasets discoverable and citable. It was then brought to the attention of the biodiversity community in 2011 as a result of a joint GBIF and Pensoft project and later implemented in the routine publishing process in all Pensoft journals.
Since then, Pensoft has been working with GBIF, and subsequently DataONE to automate the process of converting metadata into a human-readable data paper format. The novel workflow means that with only a couple of clicks, publishers of datasets on either GBIF, DataONE or any other portal storing metadata in the same format, may submit a manuscript for peer-review and open access citable publication in BDJ.
The process is simple, yet it brings a lot of benefits. Publishing data does not only mean a citable publication and, thus, credit to the authors and the repository itself, but it also provides the option to improve your work and collect opinion though peer-review. BDJ also shortens the distance between "narrative (text)" and "data" publishing.
"Metadata descriptions (e.g., data about the data) are of primary importance for data dissemination, sharing and re-use, as they give essential information on content, scope, purpose, fitness for use, authorship, usage rights, etc. to any potential user. Authoring detailed metadata in repositories can seem a tedious process, however DataONE users will now benefit from direct export of already created metadata into data paper manuscripts and have even better exposure of their work through discoverability mechanisms and scholarly citations," commented Dr Amber Budden, DataONE Director for Community Engagement and Outreach
"It is great to reap the fruits of a process that started back in 2010. The automated streamlining of biodiversity data between repositories and publisher is an elegant feature that makes publishing a data paper an easy and rewarding process to crown scientists data collection efforts and ensure its use and re-use," added Prof. Lyubomir Penev, Managing Director of Pensoft.
More detailed information on how data authors could use the workflow can be found on the Pensoft blog.
References:
Chavan V, Penev L (2011) The data paper: a mechanism to incentivize data publishing in biodiversity science. BMC Bioinformatics. 12(Suppl 15):S2. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-S15-S2
The work has been partially supported by the EC-FP7 EU BON project (ENV 308454, Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network) and the ITN Horizon 2020 project BIG4(Biosystematics, informatics and genomics of the big 4 insect groups: training tomorrow's researchers and entrepreneurs), under Marie Sklodovska-Curie grant agreement No. 542241.
Biodiversity Observation Networks (BONs) have recently become a hot topic on the scene of natural sciences. But what is their role in advancing our knowledge of biodiversity and associated ecosystem services?
A new paper in the Biodiversity journal uses the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON) as an example, to explain how they can fill in gaps and address existing barriers in knowledge through implementing an integrated biodiversity information framework.
Biodiversity supports essential ecosystem services that are key to human well-being. The ongoing global biodiversity decline is a threat to humans, particularly in developing countries.
The Aichi biodiversity targets of the United Nations' Strategic Plan for Biodiversity set ambitious goals for protecting biodiversity from further decline, but gaps in knowledge still sit in the way of monitoring progress, hindering the assessment of the current status and future trends of biodiversity.
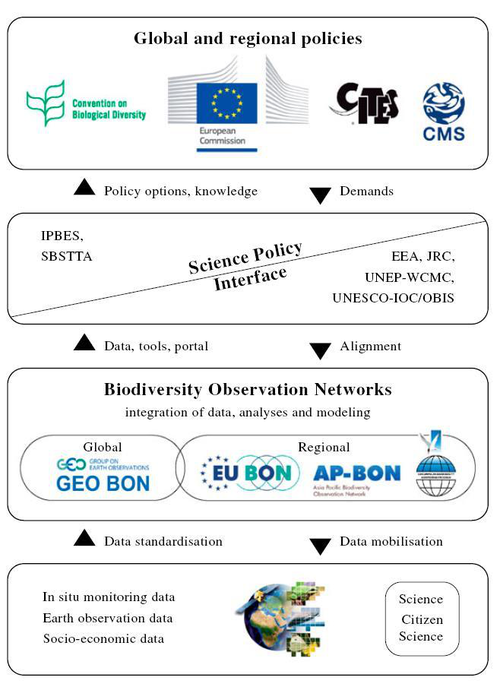 There is an urgent need for a paradigm shift with regards to how biodiversity data are collected, stored, shared and streamlined in order to tackle many sustainable development challenges ahead.
There is an urgent need for a paradigm shift with regards to how biodiversity data are collected, stored, shared and streamlined in order to tackle many sustainable development challenges ahead.
Solving issues of biodiversity knowledge gaps and data reuse are a main focus of the EU BON project and provide a European contribution to GEO (Group on Earth Observations) and the wider Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS).
The EU BON project aims at addressing the need for a shift towards an integrative biodiversity information framework, starting from collection to the final interpretation and packaging of data.
At the centre of the EU BON's efforts is promoting and adopting existing standards of good practice and integrating data within a single biodiversity portal in order to make it discoverable, accessible and digestible. The aim of the portal is to collect and standardize existing data sources, as well as to work towards translating and visualizing the collected raw data to show trends and prognoses useful to policy and society.
"Biodiversity data, information and knowledge are diverse, dispersed and disparate. It is hard for a non-specialist to make sense of raw data and often separate data sets and gaps in data prevent effective policy reporting. This is why progress towards the Aichi targets is often hard to calculate, and where BONs can play a central role by working towards standardization to achieve true interoperability of data sets." explains the lead author Dr. Florian T. Wetzel,Museum für Naturkunde (MfN), Berlin.
"For advancing with the biodiversity challenge and the Aichi Targets globally, regional BONs are needed, and this is where EU BON attempts to make a difference for Europe" adds Dr. Christoph L. Häuser, EU BON coordinator and Deputy Director General at MfN, Berlin.
###
Original Source:
Florian T. Wetzel, Hannu Saarenmaa, Eugenie Regan, Corinne S. Martin, Patricia Mergen, Larissa Smirnova, Éamonn Ó Tuama, Francisco A. García Camacho, Anke Hoffmann, Katrin Vohland & Christoph L. Häuser (2015): The roles and contributions of Biodiversity Observation Networks (BONs) in better tracking progress to 2020 biodiversity targets: a European case study, Biodiversity, DOI: 10.1080/14888386.2015.1075902
What are the threats for biodiversity from global to local spatial scales? How might human beings succeed in fighting biodiversity loss?
EU BON partners, Annapaola Rizzoli and Duccio Rocchini give a TEDx talk on extreme biodiversity in space and time at 2200 metres in the Pale di San Martino on September 6, organized by TEDxTrento (soon will be also available with English subtitles).
Learn more here.
The fifth EU BON Policy brief focuses on the need for open data in biodiversity monitoring. The Group on Earth Observation’s Biodiversity Observation Network, of which EU BON is a part, has a vision to better monitor and manage the global biosphere for our common good. This creates research challenges that require use of all appropriate data. Yet, access to data is impaired because, traditionally, few data are released, they are often locked up in traditional scientific literature, or because of concerns over intellectual property rights.
Because of this, EU BON endorses the free and open exchange of data and knowledge in accordance with the "Joint Declaration on Open Science for the 21st Century", especially in regard to scientific information produced in Europe as outlined by the European Commission.
Find out more in the Policy Brief below:
We are happy to announce that earlier this summer EU BON has been selected to be featured as a successful EU-funded project. The DG Research & Innovation communication team has interviewed our project co-ordinator Christoph Häuser and the resulting article - Combining citizen and satellite biodiversity data - is now a fact!
The news item focuses on EU BON's efforts to bring together biodiversity and Earth observation data, that are accumulated from data sources ranging from the individual citizen scientist, researchers to the most technologically advanced satellites in one EU-wide initiative.
"Information on life on Earth is crucial to addressing global and local challenges, from environmental pressures and societal needs, to ecology and biodiversity research questions," commented Christoph Häuser in his interview.
View the full story on the Horizon 2020 site.
An EU BON workshop took place on 20-23 July in Manaus, Brasil for a targeted group of representatives of the different EU BON WPs or task forces. The workshop was attended by European representatives of EU BON and INPA to discuss potential options to further the integration between European teams and the Brazilian team.
Among topics discussed at the workshop were issues of designing and running biodiversity monitoring observatories (i.e. optimization and guidelines for planning biodiversity monitoring); analyses of biodiversity data to be addressed for assessing changes and patterns; and linkage of (meta-) data to EU BON portal.



Images from the workshop; Credit: William Magnusson (INPA) & Israel Peer (GlueCAD)
Being hosted in Manaus, this workshop also looked into facilitationg the integration of Brazilian and European expertise, for instance by updating about the progress made by Brazil in starting participatory resource monitoring in Brazilian National parks and the development of databases to integrate this information.
Besides presentation and discussions, INPA organized an excursion to show their log-term biodiversity monitoring field sites (RAPELD) and to explain the rationale and methodology behind their design and organization.



Images from the excursion; Credit: Charlie Marsh
A new EU BON derived open access paper looking into Earth Observations (EO) and the Aichi Targets was recently published in the journal Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation.
The paper reviews the ABTs and EBVs against direct and indirect, operational and emerging, EO data products. The review was conducted by consulting expert opinion and categorically rating the Targets based on the adequacy of currently available EO technology to build indicators per target. The potential RS-EBVs were also matched with their respective EO data products.
To summarize this information a monitoring framework is proposed where RS-EBVs are used to harmonize observations prior to the indicator stage. Potential obstacles to implementing this framework and challenges to its adoption by the wider science and policy community are discussed. Finally, upcoming satellite missions which could offer potential for assessing global biodiversity status and trends beyond the 2020 timeframe of the CBD's current Strategic Plan for Biodiversity are discussed.
Original Source:
O'Connor B. et. al. (2015) Earth observation as a tool for tracking progress towards the Aichi Biodiversity Targets. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation. DOI: 10.1002/rse2.4
The Department of Conservation Biology at the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) is offering a full-time position for a Population Biologist / Conservation Biologist (Postdoc) focussing on assessing past and future trends in species under land use and climate change and improving the design of monitoring schemes. The position will be part of EU BON.
The Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) with its 1,100 employees has gained an excellent reputation as an international competence centre for environmental sciences. We are part of the largest scientific organisation in Germany, the Helmholtz association. Our mission: Our research seeks to find a balance between social development and the long-term protection of our natural resources.
More information on the oficial job offer page: http://bit.ly/1MexC6Q
A new EU BON acknowledging special issue "Earth Observation for Ecosystems Monitoring in Space and Time: A Special Issue in Remote Sensing" published in the open access journal Remote Sensing provides a collection of important researchers in the field, as well as the most challenging aspects of the application of remote sensing to study ecosystems.
http://www.mdpi.com/journal/remotesensing/special_issues/ecosystemsmonitoring
The 9th GEO European Projects Workshop took place on 15 and 16 June 2015, in Copenhagen, Denmark. A special session dedicated to biodiversity and ecosystems was held as a part of the meeting, where EU BON and other topic relevant projects were presented.
The session was started by Gary Geller with an introduction and overview. Particularly the importance of the long-term sustainability of the projects and the linkages to the overall aims of GEO were stressed, as well as the opportunity of the session to find further synergies among the GEO-related projects.

Participants at the biodiversity and ecosystems sessions during the 9th GEO European Projects Workshop; Credit: Florian Wetzel
EU BON was presented at the meeting by the project coordinator Christoph Häuser, who outlined the core elements for an integrated biodiversity information system. There is the challenge to provide a sound framework to overcome the fragmentation of available biodiversity information to obtain better information for political decision making. EU BON with its 31 partners tackles this challenge and its main objective is to serve as a European contribution to GEO BON.
Other projects presented during the session were EU H2020 projects ECOPOTENTIAL and GLOBIS‑B, both already in the list of associated partners of EU BON. The third H2020 project presented here was SWOS, a Satellite-based Wetland Observation Service.
One of the major outcomes of the session was the agreement that further follow-ups of the discussions are needed and that the projects should have further exchange among each other.
Our family of Associated Partners has grown with three new members that joined us this month. EU BON has signed MoUs with the GLOBal Infrastructures for Supporting Biodiversity research (GLOBIS-B), the Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources of the National Research Council of Italy (IGG-CNR) and ECOPOTENTIAL: Improving Future Ecosystem Benefits through Earth Observations, The hand over took place during the 9th GEO European Projects' Workshop in Copenhagen (15 – 16 June 2015).


Left: EU BON coordinator Christoph Hauser and Anke Hoffmann handing over the MoUs to our partners from IGG-CNR and ECOPOTENIAL Antonello Provenzale, Carl Beierkuhnlein and Palma Blonda; Right: Handing over the MoU to Daniel Kissling - scientfic coordinator of GLOBIS-B; Credits: Anke Hoffmann
The GLOBIS-B project is a new H2020 project aiming to bring together biodiversity scientists with research infrastructure operators and legal interoperability experts to address the research needs and infrastructure services required to calculate Essential Biodiversity Variables (EBV) at a global scale.
ECOPOTENTIAL makes significant progress beyond the state-of-the-art and creates a unified framework for ecosystem studies and management of protected areas (PA). ECOPOTENTIAL focuses on internationally recognized PAs in Europe and beyond in a wide range of biogeographic regions, and it includes UNESCO, Natura2000 and LTER sites and Large Marine Ecosystems. Best use of Earth Observation (EO) and monitoring data is enabled by new EO open-access ecosystem data services (ECOPERNICUS).
IGG-CNR conducts studies based on mineralogy, petrology, geochemistry, geodynamics and geophysics, aimed at understanding the processes occurring both in the interior and at the surface of the Earth, and providing the fundamental knowledge for the applications (technological use of geomaterials, mitigation of the natural risks and correct management of the Earth resources for a sustainable development).
The annual EU BON General Meeting was successfully held from 1 to 4 June 2015 at the Clare College Conferencing, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
The meeting was attended by a total of 85 participants with various organizational background and relation to EU BON. Among these were almost all EU BON alongside representatives of eight associate partners and many guests.

Participants at the EU BON General Meeting, 2015; Credit: Dirk Schmeller
One of the highlights of the meeting was its very start with three inspiring keynote speakers.
Among these, Bill Sutherland from the University of Cambridge started off to give an interesting speech about the progress and future plans on combining Biodiversity science and policy. Second was Gary Geller from the GEO secretariat who talked about GEO, GEOSS and GEO BON, its vision and goals.
Later on, Johannes Peterseil from LTER-Europe shared some interesting thoughts about linking ecosystem research and earth observation through the cooperation between LTER-Europe and EU BON.
During the meeting other relevant projects were also introduced to all participants. These were DataOne and Species 2000/Catalogue of Life and two new EU projects Ecopotential and Globis-B.
The General Meeting included six thematic sessions on highly relevant EU BON topics, followed by many cross-task modules which led to better cooperation and communication between work packages and tasks. The exchange of experience gave new input to all work packages and set the milestones for the work ahead.
Presentations from the meeting will be uploaded shortly.
PRESENTATIONS:
AGENDA - EU BON 3rd General Assembly
Keynote speakers:
W.Sutherland - Biodiversity science and policy
G.Geller - GEO / GEOSS / GEOBON
J.Peterseil - Linking ecosystem research and earth observation
Other projects:
C.Flann - Species 2000 Catalogue of Life
EU BON presentations:
C.Haeuser - EU BON core elements for an integrated biodiversity information system
U.Koljalg - Data mobilization strategy and show case
H.Saarenmaa - European biodiversity portal
Y.Gavish - Developing EU BON's site-specific portal
E.Regan - Stakeholder requirements
I.Geijzendorffer - Context of EU BON
Selection of pictures from the meeting:





Sustainable governance of our biological resources demands reliable scientific knowledge to be accessible and applicable to the needs of society. To achieve this, the EU BON project aims to develop a European Biodiversity Observation Network that facilitates open access to biodiversity data of relevance to environmental policy, and to develop innovative platforms for sharing and conveying this information through visually effective and policy-relevant media.
As part of this endeavour, EU BON partners FishBase Information and Research Group (FIN), the Museum für Naturkunde Berlin (MfN), and the UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre collaborated to produce an infographic titled ‘Climate Change & Biodiversity: What may happen to bony fishes in the North Sea?’. This infographic explains the economic and ecological importance of bony fishes in the context of the North Sea. It also visualises potential changes to species diversity and composition over time, using habitat suitability and climate change predictions. These changes have been projected to 2100 based on modelled environmental conditions under the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s A2 emissions scenarios. The projections have direct policy relevance to Aichi Biodiversity Target 10 of the Convention on Biological Diversity, which seeks to understand trends in climatic impacts on community composition in ecosystems, and to thereby minimize these impacts.
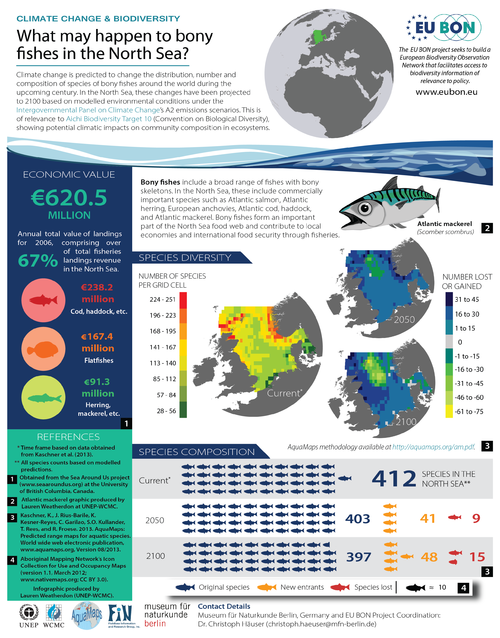
The infographic was published on the 1st June 2015 on page 26 of The Parliament Magazine’s ‘Green Week’ edition (Issue 413), which is distributed to all members of European Parliament, the European Commission, Presidency Office, Party political groups, and various other EU institutions, with over 50,000 readers worldwide.




 RSS news
RSS news


