 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
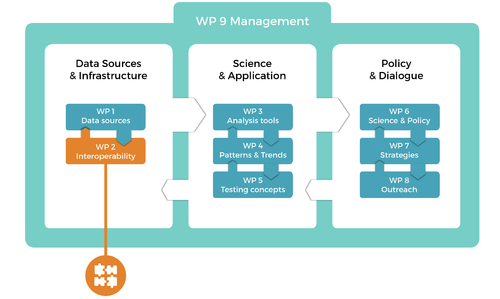
WP2 Data integration and interoperability
Objectives
-
Establish an information architecture for the EU BON project that will be compatible with the global GEO BON, INSPIRE, other European projects, and the LifeWatch research infrastructure
-
Develop data integration and interoperability between the various networks, and with new generation of data sharing tools enhance linking between observational data, ecosystem monitoring data, and remote sensing data
-
Develop new web service interfaces for data holdings using state-of-the-art standards and protocols. Register the networks on the GEOSS Common Infrastructure (GCI) using harmonised metadata
-
Develop a new portal to enable fast access to EU BON integrated data and products by researchers, decision makers and other stakeholders
-
Ensure global coordination of development efforts through an international data interoperability task force and adoption of the results through helpdesk and a comprehensive training programme
Key Messages
- The fragmentation and heterogeneity of environmental datasets and biodiversity observation systems remains a major challenge for effective data integration, analysis and access, and therefore for policy support. This work package is focussed on bringing together the fragmented data.
- This will be achieved by an effective registry system which builds on existing major resources such as GBIF, LTER, DataOne, EuMon, etc., and links them using the GEOSS Data Access Broker system. The portal of EU BON will be the public interface to the integrated data and services.
- Advancing data standards for biodiversity observation is necessary for enabling data sharing and implementation of the GEOSS Data Sharing Principles. Data standards and tools for quantitative data have now been put together, and are being rolled out by the training and support actions of EU BON.
- Data flows required for the production of Essential Biodiversity Variables need an effective, automated system. The necessary workflows for EBVs are being piloted in cooperation with other work packages.
Tasks
Task 2.1 Design of information architecture for EU BON 

Task 2.2 Improving data standards and interoperability 

Task 2.3 Tools for data sharing 

Task 2.4 Metadata registry and catalogue 

Task 2.5 European Biodiversity Portal 

Task 2.6 Technical support and helpdesk 

Task 2.7 Informatics task force and global cooperation 

Task 2.8 Training programme 

Outcomes
- Information architecture that links to other related systems and services
- New and enhanced data standards and data provider tools
- Registry system which links to GEOSS Common Infrastructure
- Portal to access integrated quantitative biodiversity observation data and workflows for Essential Biodiversity Variables
- Helpdesk and training programme
Publications
- Scholes RJ, Walters M, Turak E, Saarenmaa H, Heip CHR, Ó Tuama É, Faith DP, Mooney HA, Ferrier S, Jongman RHG, Harrison IJ, Yahara T, Pereira HM, Larigauderie A, Geller G. 2012. Building a global observing system for biodiversity. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 4: 139-146. Elsevier.
- Saarenmaa H, Schmidt J, Hugo W. 2013. Development of extended content standards for biodiversity data. European Geosciences Union (EGU) General Assembly 2013. Vienna, 8-12 April 2013. Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 15, EGU2013-6968, 2013.
- Smirnova L, Jacobsen K, Mergen P, Theeten F, Saarenmaa H. 2014. Helpdesk and training facilities at the Royal Museum for Central Africa, now EU BON oriented. TDWG 2014 Annual Conference, Jönköping, Sweden, 27-31 October 2014. Applications and Data Standards for Sustaining Biodiversity.
Contacts
Hannu Saarenmaa  |
Patricia Mergen  |
Antonio Garcia Camacho  |
Tim Robertson  |
| WP Leader | Deputy Leader, Task Leader (T2.3, T2.6, T2.8) | Task Leader (T2.1, T2.5) | Task Leader (T2.2, T2.4) |
| University of Eastern Finland (UEF) | Royal Museum for Central Africa (RMCA) | Spanish Council for Scientific Research (CSIC) | Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) |




 RSS news
RSS news NEWS
NEWS CALENDAR
CALENDAR